The patient flow process is one of the most critical aspects of running a healthcare facility efficiently. It encompasses every step a patient takes, from arrival at the clinic or hospital to discharge, including registration, triage, consultation, treatment, and follow-up.
Efficient patient flow ensures that patients receive timely care, staff workloads are balanced, and resources are utilized effectively.
Poor management of this process, on the other hand, can lead to long wait times, frustrated patients, overworked staff, and even decreased revenue for healthcare organizations.
Beyond the operational perspective, inefficient flow can impact clinical outcomes. Delays in treatment can exacerbate conditions, reduce patient satisfaction, and even affect hospital ratings.
Staff burnout increases when workloads are uneven or when resources are poorly coordinated, creating stress that can compromise care quality.
Furthermore, inefficient patient flow directly affects revenue through lost appointments, idle rooms, and underutilized staff. Implementing patient flow solutions can help streamline these processes and reduce inefficiencies.
Effective patient flow management goes beyond isolated improvements like faster check-ins or scheduling adjustments. It focuses on the entire patient journey, aligning clinical workflows, staff allocation, and resources to optimize both experience and outcomes for patients.
Modern tools like an AI medical receptionist or AI patient scheduling can support staff and improve operational efficiency.
In today’s healthcare environment, where patient expectations are higher and facilities are under pressure to do more with less, patient flow optimization is no longer optional; it’s essential.
This blog will cover the importance of the patient flow process, common challenges, key metrics, and 10 actionable strategies to optimize flow. We will also discuss the role of technology, the benefits of optimized flow, and common mistakes to avoid when implementing improvements.
By the end, healthcare administrators and clinic managers will have a clear roadmap to improve healthcare workflow efficiency, reduce issues, and enhance both staff and patient satisfaction.
Table of Contents
What Is the Patient Flow Process?
It refers to the movement of patients through healthcare facilities, from entry to exit. It is a structured approach to managing patient interactions, appointments, and transitions between departments.
A well-designed flow ensures that patients spend minimal time waiting, providers use their time efficiently, and the facility’s resources, such as exam rooms, diagnostic equipment, and staff, are optimized.
Stages of Patient Flow
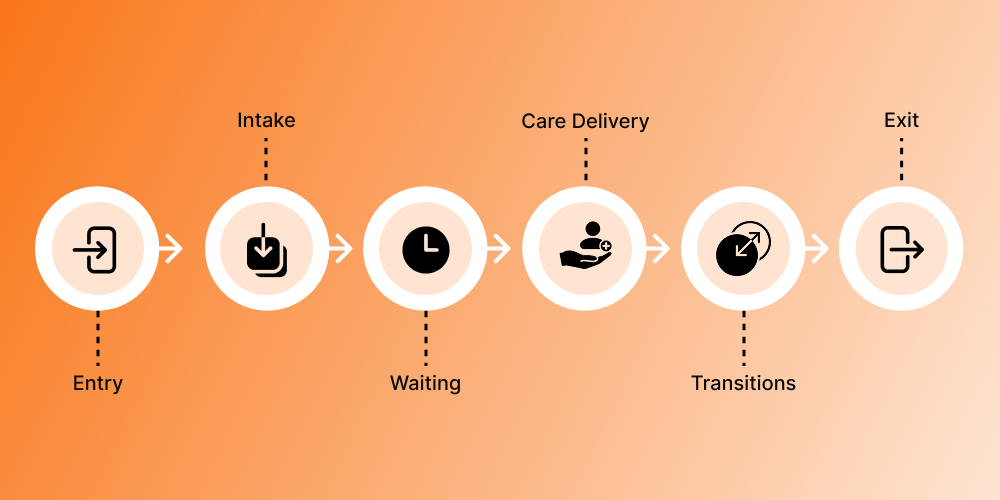
Entry: The journey begins when a patient arrives at the facility. This may involve parking, check-in, or triage. Smooth entry procedures reduce congestion and set the tone for a positive patient experience.
Intake: Collecting patient information, medical history, and insurance details. Standardized intake processes are essential for reducing errors and ensuring patients are directed to the right care quickly.
Waiting: Patients often wait between stages, such as before seeing a provider or while tests are being processed. Minimizing idle time is critical for patient throughput improvement.
Care Delivery: Interaction with providers, diagnostics, procedures, or treatments. Optimizing clinical workflow management ensures care is delivered efficiently without compromising quality.
Transitions: Movement between departments, staff handoffs, or referrals. Smooth transitions prevent delays and errors that can disrupt the entire flow.
Exit: Discharge, checkout, or post-visit instructions. Efficient exit procedures reduce congestion at the front desk and free up staff to attend to incoming patients.
Differences Across Healthcare Settings
Clinics: Often high-volume but low-acuity; focus is on rapid intake and short consultation times. Optimizing the appointment scheduling workflow and managing waiting areas are critical. Tools like AI appointment setter can help improve scheduling efficiency.
Hospitals: Complex facilities with multi-department journeys; patient flow must coordinate admissions, inpatient care, diagnostics, and discharge. Inefficiencies in one department can ripple throughout the hospital.
Outpatient Centers: Procedure-focused settings, where patient flow depends on precise timing, prep, and recovery. Patient flow optimization here relies heavily on coordination and resource allocation.
Core components of an effective patient flow process include time, capacity, resources, and coordination. Ensuring the right mix of staff, equipment, and rooms, along with clear communication, is the foundation of healthcare workflow efficiency.
Common Patient Flow Challenges in Healthcare
Even with experienced staff, healthcare facilities face recurring challenges in patient flow:
- Long patient wait times: Delays at registration, triage, or provider consultation frustrate patients and may affect satisfaction scores.
- Front desk blockage: Inefficient intake procedures can cause congestion at the point of entry.
- Poor scheduling alignment: Overbooked or poorly staggered appointments create idle providers and crowded waiting areas.
- Exam room underutilization: Empty rooms waste resources while patients wait elsewhere.
- Provider idle time vs. overload: Uneven workload distribution can overburden some staff while others are underutilized.
- Inefficient handoffs between staff: Miscommunication can result in duplicated tasks or missed steps.
- Delayed discharges or visit closures: Slow exit procedures prevent incoming patients from being seen in a timely manner.
For example, a busy clinic may experience delays because multiple patients with complex conditions are scheduled at the same time while simpler visits are left waiting. Implementing proper patient flow management ensures that such congestions are minimized and patients move efficiently from stage to stage.
Key Metrics Used to Measure Patient Flow Performance
Measuring performance is essential to effective patient flow optimization. Common metrics include:
- Patient wait time: The duration between arrival and the start of clinical interaction. Tracking this helps identify blockages.
- Visit turnaround time: Total duration of the patient’s journey, including waiting, treatment, and discharge.
- Patient throughput: Number of patients seen in a given time frame. Increasing throughput while maintaining quality is a key goal.
- Exam room utilization: Percentage of time rooms are occupied for active patient care.
- Provider utilization: Measures staff workload and ensures even distribution.
- Schedule gaps: Identifies underused appointment slots in appointment scheduling workflows.
These metrics not only inform day-to-day decisions but also guide strategic planning for clinical workflow management and overall healthcare workflow efficiency.
Top 10 Strategies for Improving Patient Flow Process

Strategy 1: Standardize the Patient Intake Process
The intake process is often the first source of delays. Standardization improves accuracy and efficiency:
- Implement digital pre-registration forms
- Consistent triage protocols to prioritize patients
- Staff training on standardized intake procedures
A primary care clinic that digitized its intake forms reduced average wait times by 15 minutes per patient, boosting patient throughput improvement.
Strategy 2: Optimize Appointment Scheduling Workflows
A well-designed appointment scheduling workflow balances patient demand with provider capacity:
- Match appointment duration to patient needs
- Group similar appointments together for efficiency
- Reserve slots for urgent or walk-in patients
- Automated reminders reduce no-shows
When a specialty clinic implemented smart scheduling software, it increased daily appointments by 20% without overloading staff, demonstrating effective patient flow optimization.
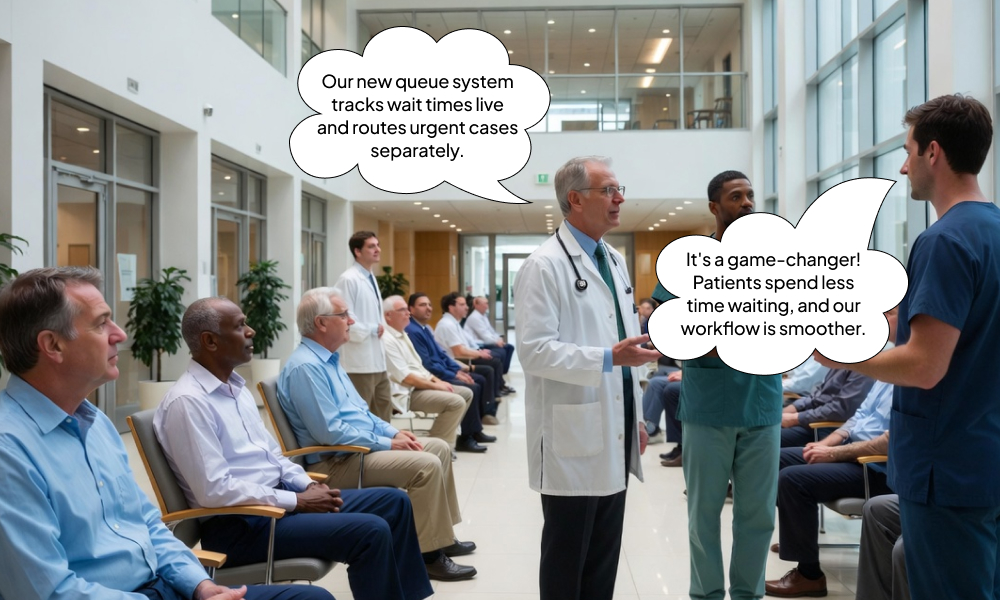

Strategy 3: Reduce Patient Wait Times Through Queue Management
Wait times significantly impact patient satisfaction. Techniques include:
- Digital wait-time displays
- Mobile check-ins and self-service kiosks
- Separate queues for urgent or high-priority patients
- Real-time monitoring to allocate staff dynamically
Efficient queue management is a core aspect of patient flow management and healthcare workflow efficiency.
Strategy 4: Improve Exam Room Utilization
Empty exam rooms reduce capacity. Solutions include:
- Dynamic room assignments based on patient and provider availability
- Coordinate cleaning and prep staff for rapid turnover
- Monitor occupancy with real-time dashboards
Better room utilization directly improves patient throughput improvement, reduces wait times, and increases revenue.
Strategy 5: Streamline Clinical Workflows
Optimizing clinical workflow management ensures care is delivered efficiently:
- Standardize care protocols to reduce variability
- Minimize redundant documentation through EHR templates
- Clearly assign roles and responsibilities
- Coordinate lab, imaging, and treatment tasks
A clinic that implemented standardized protocols for lab collection reduced patient idle time by 25%, improving overall process.

Strategy 6: Strengthen Care Coordination and Handoffs
Transitions between staff or departments can cause delays:
- Structured handoffs using standardized protocols or briefings
- Shared digital tools for seamless communication
- Staff training on concise information exchange
- Auditing handoff efficiency
Smooth transitions reduce errors, improve satisfaction, and enhance healthcare workflow efficiency.
Strategy 7: Balance Capacity and Demand
Resource mismatches create bottlenecks. Strategies include:
- Forecast patient volumes using historical data
- Adjust staffing during peak times
- Cross-train staff for multiple roles
- Flexible scheduling to manage high-demand services
Balancing capacity and demand is essential for effective patient flow management.
Strategy 8: Identify and Remove Flow Bottlenecks
Bottlenecks disrupt efficiency. Steps include:
- Process mapping of the entire patient flow process
- Data collection on frequent delays
- Targeted interventions in critical areas
- Continuous monitoring to prevent recurrence
Eliminating bottlenecks ensures patient throughput improvement and consistent care delivery.
Strategy 9: Improve Discharge and Visit Closure Processes
The final stage of care often causes delays:
- Standardize discharge instructions and paperwork
- Coordinate pharmacy, billing, and follow-ups
- Digital discharge summaries reduce front desk congestion
- Staff anticipate delays to speed exits
Optimized discharge improves patient flow management and frees capacity for new patients.

Strategy 10: Use Data and Automation to Monitor Patient Flow
Automation and analytics support ongoing patient flow optimization:
- Dashboards track wait times, throughput, and room utilization
- Predictive analytics anticipate surges in patient volume
- Automate reminders, check-ins, and documentation
- Visual dashboards help staff identify and address inefficiencies quickly
Technology ensures continuous improvement in clinical workflow management and overall healthcare workflow efficiency.
Role of Technology in Supporting Patient Flow Process
Technology plays a vital role in modern patient flow management. Tools include:
- Electronic Health Records (EHRs) to reduce redundant documentation and improve handoffs
- Scheduling software to optimize appointment workflows and reduce gaps
- Dashboards for real-time monitoring of patient location, wait times, and resource utilization
- Predictive analytics to forecast demand and adjust staffing
- Telehealth platforms to reduce in-person load and improve patient throughput improvement
Integrated technology allows continuous patient flow optimization, supports staff, and improves patient satisfaction.
Benefits of an Optimized Patient Flow Process
Optimized patient flow delivers measurable benefits:
- Shorter wait times and improved patient experience
- Higher patient throughput and reduced bottlenecks
- Balanced staff workload and reduced burnout
- Higher care quality due to efficient transitions and coordinated workflows
- Cost savings through better resource utilization
- Improved financial performance from full utilization of exam rooms and staff
Additional benefits include improved patient retention, higher ratings on patient satisfaction surveys, and better staff morale. Facilities that regularly track flow metrics can proactively identify issues and continuously improve healthcare workflow efficiency.
Improved flow can also enhance patient trust, as timely and organized care reflects professionalism and attention to patient needs.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Improving Patient Flow
Risks include:
- Treating flow as a one-time project rather than continuous improvement
- Focusing only on scheduling, ignoring intake, handoffs, and discharge
- Neglecting staff adoption of new workflows or technology
- Fixing symptoms rather than addressing systemic problems
Avoiding these mistakes ensures sustainable patient flow optimization and effective healthcare workflow efficiency.
Fostering a Continuous Improvement Culture
An optimized patient flow process is not static. Healthcare organizations should:
- Conduct regular reviews of flow metrics
- Involve staff in identifying bottlenecks and solutions
- Update workflows as patient demand or staffing changes
- Celebrate small wins to encourage adoption of improvements
A culture of continuous improvement ensures that clinical workflow management evolves with changing needs, maintaining long-term efficiency and patient satisfaction.
Conclusion
The patient flow process is essential for delivering high-quality, efficient, and patient-centered care. From entry to discharge, each stage presents opportunities for patient flow optimization.
Standardizing intake, improving scheduling, strengthening handoffs, leveraging technology, and continuous monitoring enable healthcare facilities to enhance clinical workflow management, reduce wait times, and achieve patient throughput improvement.
Efficient patient flow is not just about moving patients faster, it’s about moving them smarter, improving satisfaction, outcomes, and the overall resilience of healthcare organizations.
By adopting a systematic, data-driven approach to patient flow management and leveraging tools like patient flow solutions or AI medical receptionist, healthcare leaders can ensure that both patients and staff benefit from streamlined, effective processes, ultimately improving operational efficiency, revenue, and care quality.
FAQs
1. Why is patient flow important in healthcare settings?
It ensures timely care, reduces wait times, optimizes staff workload, and improves patient satisfaction and resource use.
2. What are the main stages of the patient flow process?
The patient flow process typically consists of the following stages:
- Entry: Patient arrival, check-in, or triage.
- Intake: Collection of patient information, medical history, and insurance details.
- Waiting: Time spent waiting for consultation, tests, or procedures.
- Care Delivery: Interaction with healthcare providers, diagnostic tests, and treatment.
- Transitions: Movement between departments or handoffs between staff.
- Exit: Discharge, checkout, or post-visit instructions.
Optimizing each stage ensures smooth progression, reduces delays, and enhances patient experience.
3. What is patient throughput in healthcare?
Patient throughput is the number of patients treated and discharged within a specific time, measuring efficiency of care and resource use.
4. How do bottlenecks impact the patient flow process?
Bottlenecks cause delays, lower patient throughput, increase wait times, and strain staff.
5. What is the difference between patient flow and clinical workflow?
Patient flow is the patient’s journey through the facility, while clinical workflow is how staff deliver care efficiently.




